Note: this article has been grouch-tested. (wink)

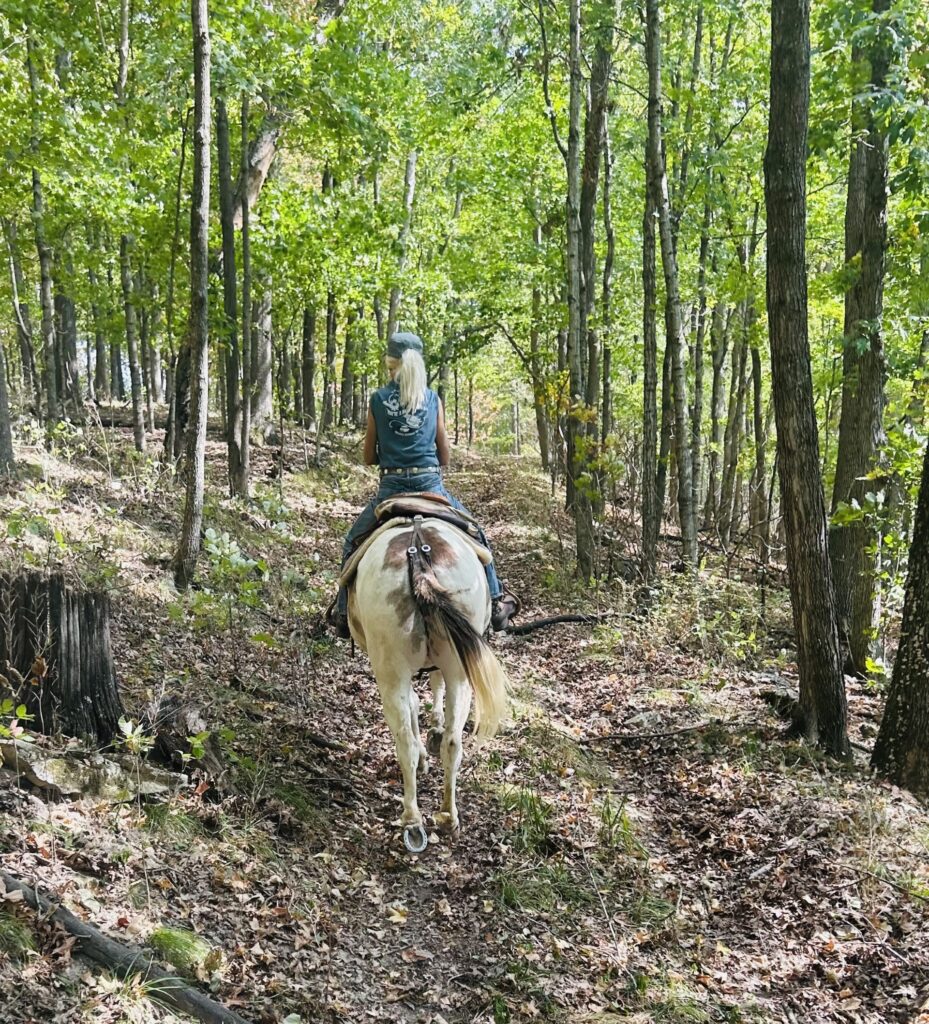
Working with mules over the years has kept me amused, captivated, fascinated, and focused, as well as being challenged. I like a challenge; it develops your creative side to problem-solving. And what better way to develop your skill set in problem-solving than by working with mules?
And now…I am creative, and I have problem-solving skills. Mules have also helped me to develop my independent side. I remember some years ago, hauling back from Colorado from a mule event, I had a palomino horse mule in the trailer; my trailer tire blew on the highway and I could not get cell service. So, I pulled the roadmap out, placed my pistol in my vest, saddled up my mule, and rode into the nearest town. A couple of hours later, I was back on my way.
Another time, the axle broke on that very same trailer while hauling through Kansas. I saddled up my mule and rode back through town to a horse motel that was a few miles down the road. The trailer was still under warranty, I was laid up for a couple of days at the horse motel. When I got home, I sold that trailer.
I suppose if I had not established myself as a leader in my mule’s life, we would have never made it out of the trailer during these emergency road incidents. You see, mules are sensitive creatures and will easily feed off your emotions. That is why your durability as a trainer is significant in working with mules. Leadership, herd boss, whatever you want to call it, the mule knows if you have grit or not. Being prepared and having confidence will help to develop your leadership skills; just remember a mule does not want to hang out with sissies. A sissy will just drag down the herd; mules know that to be safe from predators, the herd must be strong, healthy, and have it together.
A keen sense of awareness is what Mother Nature gave to the mule. In other words, mules have a high sense of self-preservation, so it is in your best interest to have it together when you approach your mule. That very mule already sized you up the very moment you walked into the corral. That mule already knows what your demeanor is for that moment; that is why you need to be established as a confident leader. I guess in a lot of ways…you are working with a smart ass.
Look, nobody likes a smart ass. They can make you look stupid. They will do things to get your attention when they are bored…because that is what mules and smartasses do. Mules will chase anything in the pasture and run from lawn equipment that they have been exposed to for years…all to work off excess energy.
You probably already know this, but mules can open doors, crawl through, or jump fences to visit in the next pasture, then return home just in time for you to feed him. And to think, this all started from boredom.
Now that you are aware that your mule is bored, you now decide to vamp up his training program. You take the time to set up an obstacle course around the barn to train your mule…except for one thing. Your mule responds by testing you…after all that is what they do. (wink) Mules will question you about the need to walk through a tire obstacle when they can easily walk around it or jump over the stuff in the first place. I mean, what’s the point?!
Again, they will question you…why get into the trailer when the other horses and mules are just tied up or hanging around? When crossing a bridge or river…is it really necessary to cross here? After all who is in charge here? This is the mindset of the mule…remember, it is his job to question you.
This is where the leadership thing comes in. It is your job to be the leader; you are the one in charge, your decision to ask the mule to do something should be based on that the mule is mentally and physically prepared to accomplish the task. It is essential that no harm will come to your mule, and you as the leader give him time to think about it to check things out. Successful mule trainers set up a situation where their mule will succeed. You want your mule to believe in you and to quietly show you that he is trying. By giving the slightest try, you the leader will give praise and encouragement to the mule. Your approach when presenting new things to your mule is important. The mule needs to be comfortable to be willing and to be able to respond to your request because they are emotional creatures. And remember, mules are supposed to think things through and check things out first because they are smarter than both their parents! The mule is simply behaving as the awesome creature that Mother Nature allowed him to develop into. After all, he is not supposed to be a horse or a donkey. He/she is just being a mule, the very smart ass that you are working with!
It is the mule’s job to think of clever ways to get out of what you want them to do. It is your job to be creative in your training program to get the mule’s curiosity stirred up while ensuring no harm will come to him. If the mule suffers injury then the deal is off. If things get boring, then your mule has no further interest in the lesson.
Now that you know you are working with a smart ass; you have your work cut out for you. You are not a whiner; you are determined to succeed. You possess the qualities of being a successful mule trainer. You are committed, conscientious, sensitive to your animals, creative, playful, logical, independent, and patient. You look for answers and you know what it takes. You realize what the mule needs physically or mentally and can follow through in giving it. OK! NOW WE’RE GETTING SOMEWHERE!
All right, you’ve got this…carry on. If you need help, you know where to find me.